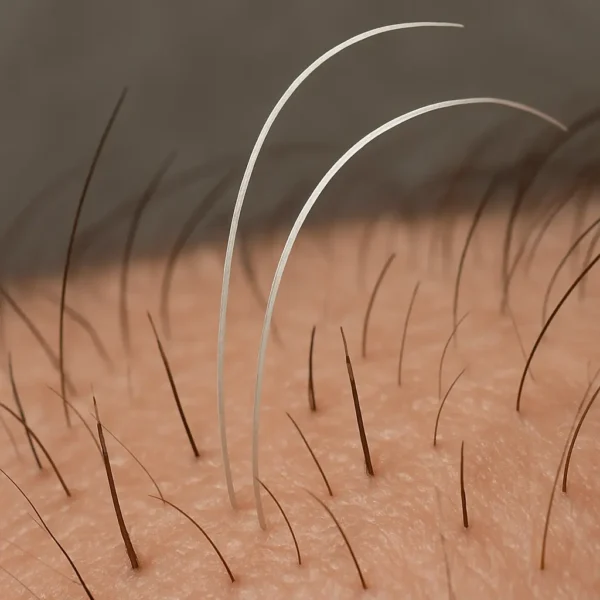
Do white hairs grow thicker and faster than pigmented hairs in humans ?
Greying is one of the most visible hallmarks of human ageing, yet its functional consequences for hair fibre biology are often overlooked. Clinicians and lay…
Insights on Hair Health, Hair Growth, and Alopecia Research
Insights on Hair Health, Hair Growth, and Alopecia Research

Greying is one of the most visible hallmarks of human ageing, yet its functional consequences for hair fibre biology are often overlooked. Clinicians and lay…

Recreational and competitive swimming exposes hair to an environment unlike any other in daily life: prolonged immersion in water that typically contains added disinfectants, dissolved…

Canities, the scientific term for the progressive loss of hair pigmentation, commonly presents as the gradual emergence of gray or white hair in individuals of…

The short answer is – possibly – but a causal effect has not been conclusively proven. Diet can influence hormonal and metabolic pathways that are…
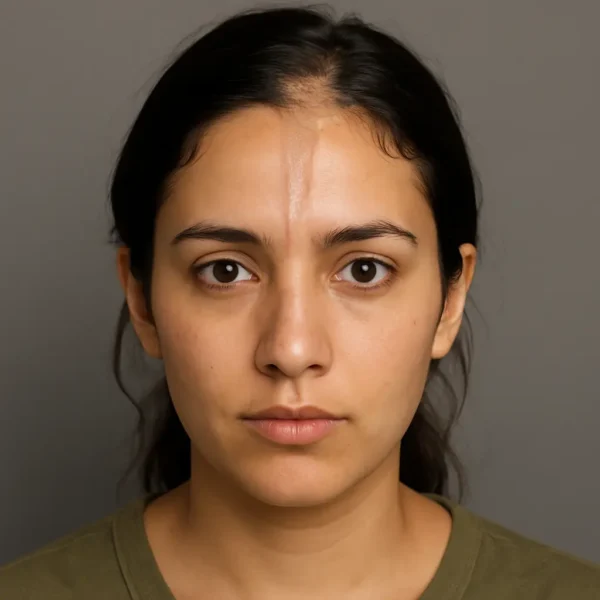

Localized scleroderma (also called morphea) is an immune-driven condition that makes the skin and nearby tissues thicken and harden. When it appears as a narrow,…
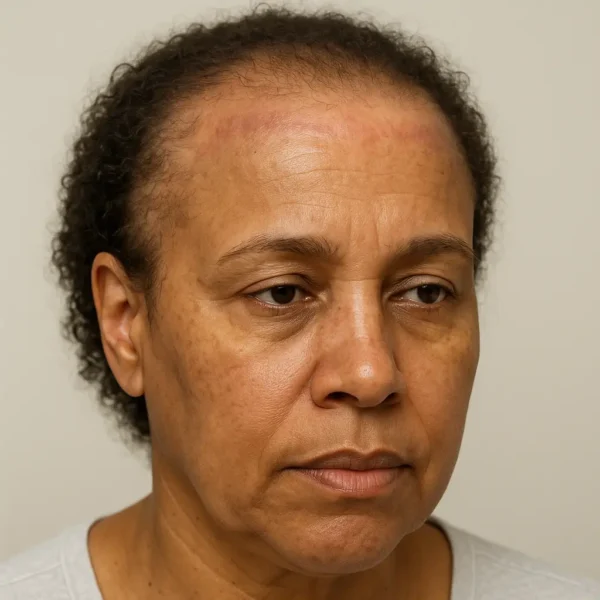

Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a primary scarring (cicatricial) alopecia that typically presents with progressive recession of the frontal and temporoparietal hairline and frequent eyebrow loss.…
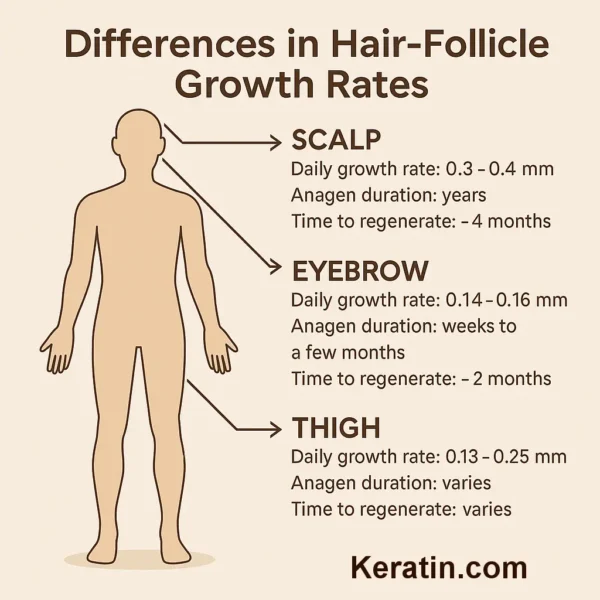
Human hair follicles are mini-organs with their own growth kinetics. They cycle through anagen (active growth), catagen (regression), and telogen (rest) and, over many cycles,…
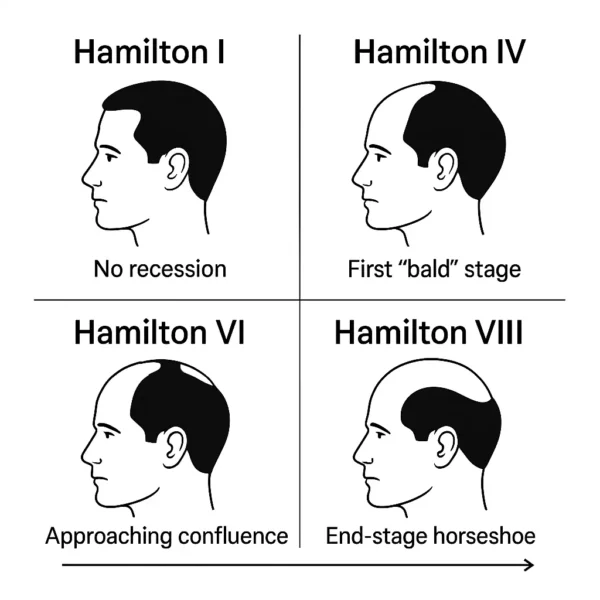
In 1951, anatomist James B. Hamilton proposed the first broadly usable scheme for grading the extent of male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia, AGA). He organized…
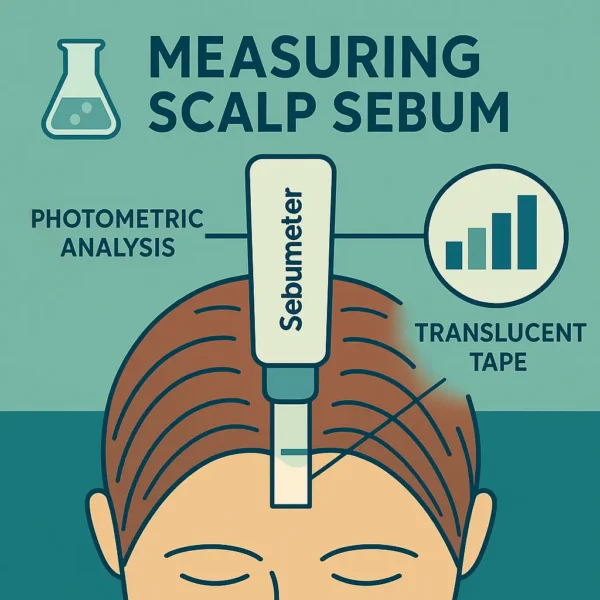
Sebaceous glands are holocrine units that synthesise and excrete a complex lipid mixture – sebum – onto the surface of skin and hair. On the…